Hair jelly, Snottie, Lion’s mane

Cyanea capillata
Hair jelly, Snottie, Lion’s mane

Cyanea capillata
Large, flat bell up to half a metre in diameter with a large ‘mop’ of fine hairlike tentacles 5-100cm long. The bell top is often white or brown with yellow, brown or reddish colouring underneath.
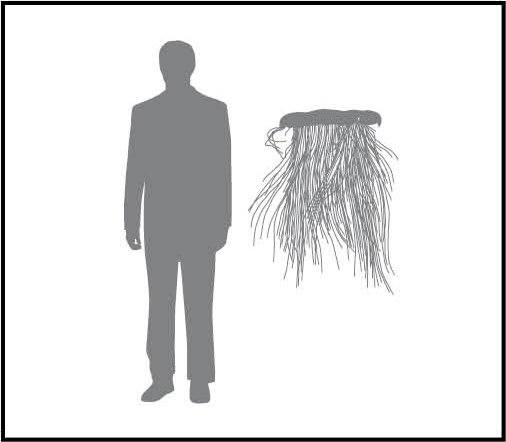

Size relative to human
Worldwide
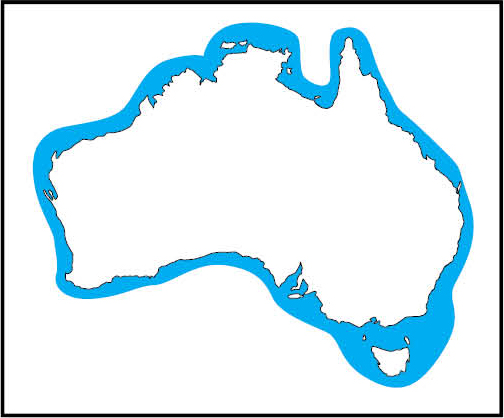
Distribution in Australian waters
Its sting causes immediate severe burning pain and whip-like marks, often with tentacles remaining on the stung area. Severe stings may cause the casualty to stop breathing and suffer cardiac arrest.
As the Cyanea is found in tropical areas, if they cannot be easily identified as such there is a risk that the sting is from a potentially lethal jellyfish and the priority is to preserve life by treating the casualty with vinegar.
Outside the tropics, where a large number of non-life threatening stings occur, the primary objective is pain relief with heat or cold.
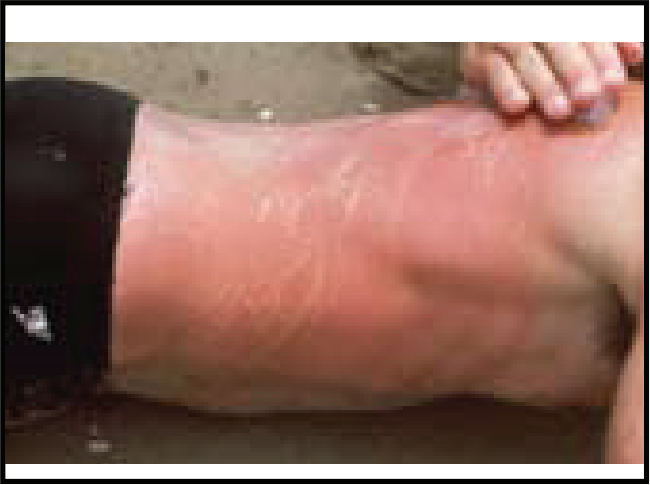
Cyanea sting